This web page was produced as an assignment for an undergraduate course at Davidson College.
My Favorite Yeast Gene
Annotated vs. Unannotated
By Jessica Lahre
Annotated Gene: SSH1/YBR283C
The annotated gene SSH1 or YBR283C is located chromosome II of Saccharomyces cerevisiae between consisting of bases 770411-768939. SSH1 has the ORF name YBR2020 and is present in 704 molecules/cell. SSH1 gene encodes for the alpha-subunit of the SSH1 translocon complex in the endoplasmic reticulum called SSH1p or Sec61 protein homolog (SGD YBR283C: Summary 2006; UniPort P38353 2006; Finke et al. 1996). Its function involves protein transport, co-translational targeting, and probable maintenance of telomeres (SGD). The SSH1p has 490 amino acids with a molecular weight of 53,311 Da and an isoelectric point of 8.18 (UniPort P38353).
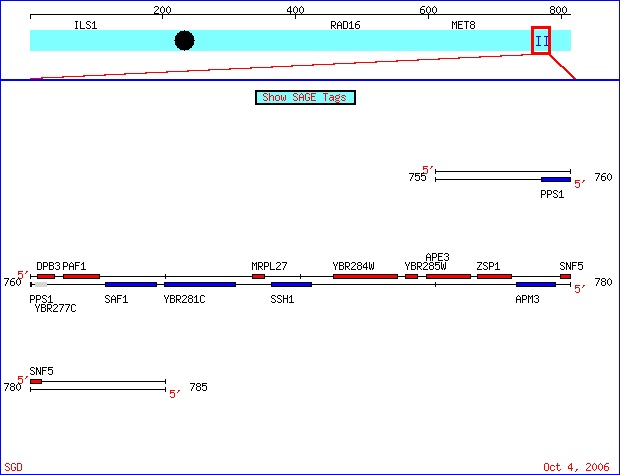
Figure 1. Saccharomyces cerevisiae Chromosome II. This ORF map of Chromosome IIof Saccharomyces cerevisiae taken from SGD shows SSH1 gene (in blue) and YBR285W (in red). Image from http://db.yeastgenome.org/cgi-bin/ORFMAP/ORFmap?dbid=S000000487.
SSH1 Amino Acid Sequence: MSGFRLIDIV KPILPILPEV ELPFEKLP DKIVYTIFAG LIYLFAQFPL VGLPKATTPN VNDPIYFLRG VFGCEPRTLL EFGLFPNISS GLILQLLAGL KVIKVNFKIQ SDRELFQSLT KVFAIVQYVI LTNIFIFAGY FGDDLSVVQI GLINFQLVGA GIFTTLLAEV IDKGFGFSSG AMIINTVVIA TNLVADTFGV SQIKVGEDDQ TEAQGALINL IQGLRSKHKT FIGGIISAFN RDYLPNLTTT IIVLAIAIIV CYLQSVRVEL PIRSTRARGT NNVYPIKLLY TGCLSVLFSY TILFYIHIFA FVLIQLVAKN EPTHIICKIM GHYENANNLL AVPTFPLSLL APPTSFFKGV TQQPLTFITY SAFILVTGIW FADKWQAISG SSARDVALEF KDQGITLMGR REQNVAKELN KVIPIAAVTG ASVLSLITVI GESLGLKGKA AGIVVGIAGG FSLLEVITIE YQQSGGQSAL NQVLGVPGAM (Sequence from http://db.yeastgenome.org/cgi-bin/protein/proteinPage.pl?dbid=S000000487)
Cellular Component
SSH1p is located in the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) and the nuclear envelop of the ER network, specifically in the translocon complex. As seen with the Kyte-Doolittle Hydropathy Plot and Transmembrane Domain Graph from SGD, there are 9 transmembrane domains. (SGD YBR283C: Protein 2006)
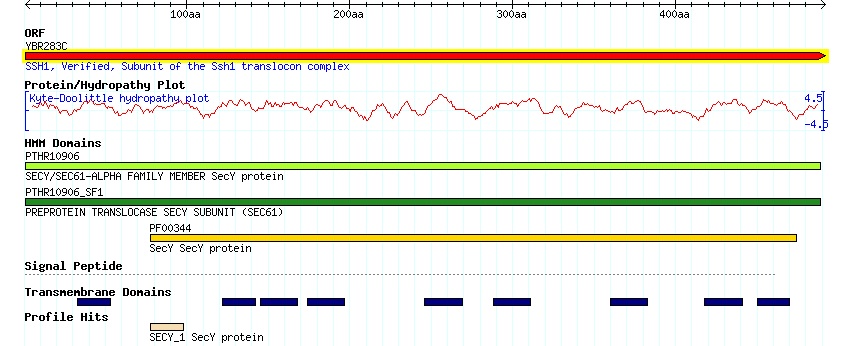
Figure 2. SSH1 Kyte-Doolittle Hydropathy Plot. The Kyte-Doolittle Hydropathy Plot from SGD shows here that there are 9 potential domains were transmembranes are located on the SSH1 protein. You can also see the similarities bettween SSH1 and the Sec61 proteins. Image from http://db.yeastgenome.org/cgi-bin/protein/domainPage.pl?dbid=S000000487.
Biological Process
SSH1p is a co-translational targeting protein to the membrane of the ER. It is part of the trimeric complex with SBH2p and SSS1p in a second co-translational pathway. Another pathway involved in both co-translation and post translation of ribosomes consists of Sec61p, SSH1p homolog, SBH1p, SBH2p homolog, and SSS1p (Finke et al.). While the exact function of SSH1p in the co-translational pathway is still unknown, it is hypothesized that instead of pushing or pulling a growing polypeptide chain through a membrane, there is a one-way transmembrane channel that only allows the chain to grow through it (Finke et al.). It has also been inferred by the mutant phenotype that SSH1 gene is involved in telomere maintenance.
Molecular Function
SSH1p acts as a protein transporter channel allowing proteins to move into, out of, and within ER. SSH1p and its homolog Sec61p are involved in co-translation of protein on the ER. It is known through systematic deletion and homozygous systematic deletion studies that SSH1 is not an essential gene, but species’ growth rate is reduced (SGD YBR283C: Summary). SSH1p and Sec61p have similar in their cytosolic loop domains, which interact with the ribosomes, but differ at their luminal domains (Finke et al.)
Unannotated Gene: YBR285W
The unannotated gene is YBR285W, located in the same region of chromosome II as SSH1 of Saccharomyces cerevisiae as shown in figure 1. The protein that YBR285 encodes for has 144 amino acids, a molecular weight of 16,833 Da, and an isoelectric point of 7.95 (UniPort P38354). The cellular component, biological process, and molecular function of YBR285Wp is unknown.
YBR285W Amino Acid Sequence: mtifsrfsyf dslfsfkkqe pspieiiycn enngfiniks lesptddsme adishremat iltrnrnnlg kvaidkkgvn nhcidlnelk kglvanehkl dndnstrhqn tyspedsvef drfddkqsri lkcstrrsyl rykk (Sequence from http://db.yeastgenome.org/cgi-bin/protein/proteinPage.pl?dbid=S000000489.
Cellular Component
YBR285W encodes for a putative protein with an unknown function. It is believed that it is located in the cytoplasm because it has no known transmembrane domains (SGD YBR285W 2006: Summary & Kye-Doolittle 2006).
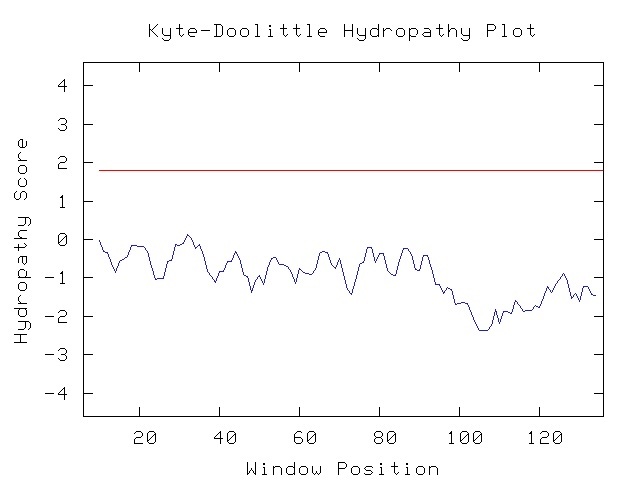
Figure 3. YBR285 Kyte-Doolittle Hydropathy Plot. This Kyte-Doolittle Hydropathy Plot of YBR285W, which shows domains of YBR285p that are most likely transmembrane domains. Peaks above 1.8 on this 19 window size would mean a transmembrane. (Kyte-Doolittle 2006)
Biological Process and Molecular Function
Its only paralog match from SSDB Paralog Search is YJL029C in Saccharomyces cerevisiae, which encodes for a protein involved in vacuolar protein sorting. Thus YBR285W and YJL029C could have similar functions in the Golgi complex because of possible evolutionary similarities. Saccharomyces cerevisiae is still viable if there is systematic deletion of YBR285W making it a nonessential gene. NCBI’s Conserved domain and Homologene returned not hits for YBR285W.
The BLASTp search brought up YBR287W found in Saccharomyces cerevisiae before YBR285W.
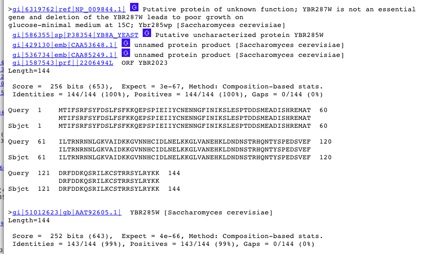
Figure4. BLASTp results for YBR285W amino acid sequence.The results from the BLASTp YBR285W amino acid sequence displayed YBR287W before YBR285W.
References
Finke, K. et al. (1996). A second trimeric complex containing homologs of Sec61p complex function in protein transport across the ER membrane of S. cerevisiae. The EMBO Journal. 3 (7): 1482-1492
Kye-Doolittle Hydopathy Plot. <http://gcat.davidson.edu/DGPB/kd/kyte-doolittle.htm>. Accessed 2006 Oct 5.
[NCBI] National Center for Biological Technology. 2006 Sept. <http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/>. Accessed 2006 Oct 2.
SGD. 2006 Oct. SSH1/YBR283C: SGD ORF Map.<http://db.yeastgenome.org/cgi-bin/ORFMAP/ORFmap?dbid=S000000487>.Accessed 2006 Oct. 4.
SGD. 2006 Oct. SSH1/YBR283C: Protein.<http://db.yeastgenome.org/cgi-bin/protein/domainPage.pl?dbid=S000000487>.Accessed 2006 Oct. 2.
SGD. 2006 Oct. SSH1/YBR283C: Summary.<http://db.yeastgenome.org/cgi-bin/locus.pl?locus=SSH1>.Accessed 2006 Oct. 2.
SGD. 2006 Oct. YBR285W: Protein.<http://db.yeastgenome.org/cgi-bin/protein/proteinPage.pl?dbid=S000000489>.Accessed 2006 Oct. 2.
SGD. 2006 Oct. YBR285W: Summary.<http://db.yeastgenome.org/cgi-bin/locus.pl?dbid=S000000489>.Accessed 2006 Oct. 2.
SSDB. 2006. SSDB KEGG Saccharomyces cerevisiae YJL029C.<http://www.genome.jp/dbget-bin/www_bget?sce:YJL029C>. Accessed 2006 Oct. 5.
SSDB. 2006. SSDB Paralog Search. <http://www.genome.jp/ssdb-bin/ssdb_paralog?org_gene=sce:YBR285W>. Accessed 2006 Oct. 5.
[UniPort]Universal Protein Resource.2006. P38354. <http://www.pir.uniprot.org/cgi-bin/upEntry?id=P38354 >. Accessed 2006 Oct. 5.
[UniPort]Universal Protein Resource.2006. P38353. <http://www.pir.uniprot.org/cgi-bin/upEntry?id=P38353>. Accessed 2006 Oct. 5.
For more information, please refer to the
Davidson College Genomics Home Page
Davidson College Biology Home Page
Back to my Home Page
E-mail me any comments or concerns
© Copyright 2006 Department of Biology, Davidson College, Davidson, NC 28035