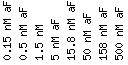This web page was produced as an assignment for an
undergraduate course at Davidson College.
DNA Microarray Data for FAR1
and YBR293W
This web page investigates the
expression of two Saccharomyces cerevisiae genes—FAR1 and YBR293W and is
a continuation of Assignment 2-My Favorite Yeast Genes: FAR1 and YBR293W.
DNA microarrays can be used to
measure the level of gene transcription.
The transcriptional response of a gene can change depending on the
genomic shift of the cell. The microarray
technology compares a control and an experimental transcriptome to see if
various genes are induced, repressed, or unchanged compared to a control under
a range of conditions.
This is the scale that was
used in the following seven DNA microarrays
to determine the expression
patterns of FAR1 and YBR293W.
Scale : (fold
repression/induction)
![]()
The
seven DNA microarrays are as follows:
DNA microarray 1: Expression at different alpha-factor concentrations (Rosetta Inpharmatics). This experiment investigates signal transduction during yeast pheromone response due to increased concentrations of alpha-factor, a mating pheromone.
DNA microarray 2: Expression in response to alpha-factor (Rosetta Inpharmatics). This experiment was actually the same as that completed for microarray1, however the data was evaluated according to the effect of alpha-factor on the yeast genome over time.
DNA microarray 3: Expression in response to
DNA-damaging agents (Stanford University).
This experiment
compared the expression of wild-type and Mec1 pathway-deficient mutants under
normal growth conditions and as a reaction to methylation and ionizing
radiation. Methylation stops
transcription and radiation increases the mutation rate. Mec1 is responsible for transducing the damage
signal that arrests the cell cycle and initiates DNA repair.
DNA microarray 4: Expression during the cell cycle (Stanford University). This experiment arrested synchronized yeast cells in various stages of the cell cycle in order to determine the expression of genes that had previously exhibited variable transcription levels during the cell cycle.
DNA
microarray 5: Expression
during the diauxic shift (Stanford University). This experiment explores the effects of a
diauxic shift on the metabolism of yeast.
The effects of a shift from aerobic respiration to anaerobic respiration
on the glucose metabolism of yeast was analyzed.
DNA microarray 6: Evolution of expression during glucose limitation (Stanford University). The transcriptional changes between evolved strains of yeast and their common ancestor were compared under aerobic, glucose-limiting conditions.
DNA microarray 7: Expression during sporulation (Stanford University). This experiment looks at changes in gene expression during sporulation, which includes both meiosis and spore morphogenesis.
FAR1
|
This annotated gene codes a
cyclin-dependent protein kinase inhibitor involved in cell cycle arrest. For more information about this gene and its
protein product see Assignment
2-My Favorite Yeast Genes: FAR1 and YBR293W.
Figure 1. Cluster from DNA Microarray 1: Expression at different alpha-factor concentrations.This DNA microarray depicts genes
with similar expression patterns when various concentrations of alpha-factor
were present. FAR1 was induced with
increasing concentrations of the mating pheromone, alpha-factor. This seems logical since the transcription
of FAR1 was found to be induced by the secretion of the alpha-factor mating
pheroomone (Peter and Herskowitz 1994).The other genes sharing this same
pattern of induction were genes involved with reproduction in various
capacities. Figure was taken from http://genome-www4.stanford.edu/cgi-bin/SGD/expression/expressionConnection.pl.
|
Orf |
|
Gene |
|
|
|
Process |
|
Function |
|
Component |
|
|
FAR1 |
|
|
cell cycle arrest |
|
cyclin-dependent protein
kinase inhibitor |
|
nucleus* |
||
|
|
DSE1 |
|
|
biological_process unknown |
|
molecular_function unknown |
|
not yet annotated |
||
|
|
|
|
|
biological_process unknown |
|
molecular_function unknown |
|
cellular_component unknown |
||
|
|
|
|
|
biological_process unknown |
|
molecular_function unknown |
|
not yet annotated |
||
|
|
ASG7 |
|
|
mating (sensu
Saccharomyces) |
|
molecular_function unknown |
|
cellular_component unknown |
||
|
|
|
|
|
biological_process unknown |
|
molecular_function unknown |
|
not yet annotated |
||
|
|
NUP159 |
|
|
not yet annotated |
|
not yet annotated |
|
not yet annotated |
||
|
|
PRM2 |
|
|
mating (sensu
Saccharomyces) |
|
molecular_function unknown |
|
integral membrane protein |
||
|
|
PRP39 |
|
|
mRNA splicing |
|
not yet annotated |
|
not yet annotated |
||
|
|
DOT5 |
|
|
transcription |
|
not yet annotated |
|
not yet annotated |
||
|
|
PRM1 |
|
|
cell-cell fusion |
|
molecular_function unknown |
|
integral membrane protein* |
||
|
|
PRM5 |
|
|
mating (sensu
Saccharomyces) |
|
molecular_function unknown |
|
integral membrane protein |
||
|
|
|
|
|
biological_process unknown |
|
molecular_function unknown |
|
not yet annotated |
||
|
|
|
|
|
biological_process unknown |
|
molecular_function unknown |
|
not yet annotated |
||
|
|
KAR4 |
|
|
meiosis* |
|
transcription factor |
|
nucleus |
||
|
|
SGN1 |
|
|
biological_process unknown |
|
molecular_function unknown |
|
not yet annotated |
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
HYM1 |
|
|
biological_process unknown |
|
molecular_function unknown |
|
not yet annotated |
||
|
|
|
|
|
biological_process unknown |
|
molecular_function unknown |
|
not yet annotated |
||
|
|
AFR1 |
|
|
signal transduction of
mating signal (sensu Saccharomyces)* |
|
receptor signaling protein |
|
shmoo |
||
|
|
KAR5 |
|
|
nuclear fusion |
|
molecular |
|
|
Figure 2. Cluster from DNA microarray 2: Expression in response to
alpha-factor. FAR1 is constantly
inducted over time when exposed to alpha-factor. This microarray data serves as a confirmation of Peter and
Herskowitz’s findings in 1994. Most of
the other genes that are similarly expressed are involved in yeast
propagation. Figure was taken from http://genome-www4.stanford.edu/cgi-bin/SGD/expression/expressionConnection.pl.
|
Orf |
|
Gene |
|
|
|
Process |
|
Function |
|
Component |
|
|
FAR1 |
|
|
cell cycle arrest |
|
cyclin-dependent protein
kinase inhibitor |
|
nucleus* |
||
|
|
STE2 |
|
|
pheromone response (sensu
Saccharomyces) |
|
mating-type alpha-factor
pheromone receptor |
|
integral plasma membrane
protein |
||
|
|
|
|
|
biological_process unknown |
|
molecular_function unknown |
|
not yet annotated |
||
|
|
PRM6 |
|
|
mating (sensu
Saccharomyces) |
|
molecular_function unknown |
|
integral membrane protein |
||
|
|
AXL1 |
|
|
axial budding* |
|
metalloendopeptidase |
|
intracellular |
||
|
|
STE4 |
|
|
signal transduction of
mating signal (sensu Saccharomyces) |
|
heterotrimeric G-protein
GTPase, beta subunit |
|
plasma membrane* |
||
|
|
FUS1 |
|
|
conjugation (sensu
Saccharomyces) |
|
molecular_function unknown |
|
plasma membrane |
||
|
|
PRP39 |
|
|
mRNA splicing |
|
not yet annotated |
|
not yet annotated |
||
|
|
SUT1 |
|
|
transport |
|
not yet annotated |
|
not yet annotated |
||
|
|
FUS3 |
|
|
protein amino acid
phosphorylation* |
|
MAP kinase |
|
nucleus* |
||
|
|
CHS7 |
|
|
not yet annotated |
|
not yet annotated |
|
not yet annotated |
||
|
|
GPA1 |
|
|
signal transduction of
mating signal (sensu Saccharomyces) |
|
heterotrimeric G-protein
GTPase, alpha subunit |
|
plasma membrane* |
||
|
|
SST2 |
|
|
signal transduction* |
|
GTPase activator |
|
plasma membrane |
||
|
|
SKT5 |
|
|
cytokinesis* |
|
enzyme activator |
|
cytokinetic ring (sensu
Saccharomyces) |
||
|
|
PRM1 |
|
|
cell-cell fusion |
|
molecular_function unknown |
|
integral membrane protein* |
||
|
|
SLI15 |
|
|
not yet annotated |
|
molecular_function unknown |
|
not yet annotated |
||
|
|
MFA2 |
|
|
mating (sensu
Saccharomyces) |
|
not yet annotated |
|
not yet annotated |
||
|
|
HSL7 |
|
|
bud growth* |
|
protein kinase inhibitor |
|
cytokinetic ring (sensu
Saccharomyces) |
||
|
|
|
|
|
biological_process unknown |
|
molecular_function unknown |
|
not yet annotated |
||
|
|
CUP9 |
|
|
not yet annotated |
|
not yet annotated |
|
not yet annotated |
||
|
|
|
|
|
biological_process unknown |
|
molecular_function unknown |
|
not yet annotated |
Figure 3. Cluster from DNA microarray 3: Expression in response to
DNA-damaging agents. This set of
genes seems to be expressed the same in both mutant and wild-type cells. When the cells are first exposed to the DNA-damaging
agents, their expression is similar to the controls. However, as time progresses the genes become repressed. FAR1 is not involved in DNA repair, so it
makes since that it would be repressed in this time of stress so that all
resources can go toward the transcription of the genes that are involved in
removing mutations or cell apoptosis.
Mec1 is responsible for transducing the damage signal that arrests the
cell cycle and initiates DNA repair.
Mec1 mutants would not be able to arrest the cell cycle, an event in
which FAR1 is involved. It would seem
that Mec1 mutants would be repressed for the expression of FAR1 more so than
wild-type yeast. Perhaps, FAR1 is not
actually inhibited in Mec1 mutants and that these two genes are involved in
slightly different pathways toward cell arrest. Figure was taken from http://genome-www4.stanford.edu/cgi-bin/SGD/expression/expressionConnection.pl.
|
Orf |
|
Gene |
|
|
|
Process |
|
Function |
|
Component |
|
|
FAR1 |
|
|
cell cycle arrest |
|
cyclin-dependent protein
kinase inhibitor |
|
nucleus* |
||
|
|
HST3 |
|
|
not yet annotated |
|
molecular_function unknown |
|
not yet annotated |
||
|
|
SUN4 |
|
|
not yet annotated |
|
molecular_function unknown |
|
not yet annotated |
||
|
|
STE12 |
|
|
pseudohyphal growth* |
|
transcription factor |
|
nucleus |
||
|
|
|
|
|
biological_process unknown |
|
molecular_function unknown |
|
not yet annotated |
Figure 4. Cluster from DNA microarray 4: Expression during the cell
cycle. As the cell cycles, this set
of genes cycles through induction and repression. FAR1 should be induced before the G1 phase where it stops the
cell cycle and it should be repressed before the S phase. Figure was taken from http://genome-www4.stanford.edu/cgi-bin/SGD/expression/expressionConnection.pl.
|
Name |
Score |
Peak |
|
|
6.488 |
M |
|
|
|
6.566 |
M/G1 |
|
|
|
7.368 |
M/G1 |
|
|
|
9.591 |
M |
|
|
|
11.64 |
M |
|
|
|
6.09 |
M |
|
|
|
6.751 |
M/G1 |
|
|
|
4.634 |
M/G1 |
|
|
|
11.8 |
M/G1 |
|
|
|
5.955 |
M/G1 |
|
|
|
5.661 |
M/G1 |
|
Figure 5. Cluster from DNA microarray 5: Expression during the diauxic
shift. All of the genes in this set
are repressed after 18.5 hours of the diauxic shift. The majority of the genes code for ribosomal structural proteins. A gene that establishes cell polarity is
also included in this set. FAR1 may
also play a role in the polarized orientation of growth during mating (Butty et
al. 1998). Figure was taken from http://genome-www4.stanford.edu/cgi-bin/SGD/expression/expressionConnection.pl.
|
Orf |
|
Gene |
|
|
|
Process
|
|
Function |
|
Component |
|
|
FAR1 |
|
|
cell cycle arrest |
|
cyclin-dependent protein
kinase inhibitor |
|
nucleus* |
||
|
|
|
|
|
biological_process unknown |
|
molecular_function unknown |
|
not yet annotated |
||
|
|
MYO2 |
|
|
establishment of cell
polarity (sensu Saccharomyces)* |
|
microfilament motor |
|
actin cap (sensu
Saccharomyces)* |
||
|
|
TRS20 |
|
|
not yet annotated |
|
not yet annotated |
|
not yet annotated |
||
|
|
|
|
|
biological_process unknown |
|
molecular_function unknown |
|
not yet annotated |
||
|
|
SEC63 |
|
|
SRP-dependent,
co-translational membrane targeting, translocation* |
|
signal recognition particle
receptor |
|
signal recognition particle
receptor |
||
|
|
ADE6 |
|
|
not yet annotated |
|
phosphoribosylformylglycinamidine
synthase |
|
not yet annotated |
||
|
|
RPL24B |
|
|
protein biosynthesis |
|
structural protein of
ribosome* |
|
cytosolic large ribosomal
(60S) subunit |
||
|
|
NUP157 |
|
|
mRNA-nucleus export* |
|
structural protein |
|
nuclear pore |
||
|
|
BUD28 |
|
|
biological_process unknown |
|
molecular_function unknown |
|
cellular_component unknown |
||
|
|
RPS7B |
|
|
protein biosynthesis |
|
structural protein of
ribosome |
|
cytosolic small ribosomal
(40S) subunit |
||
|
|
SCW10 |
|
|
mating (sensu
Saccharomyces) |
|
glucosidase |
|
cell wall (sensu Fungi) |
||
|
|
RPL8B |
|
|
protein biosynthesis |
|
structural protein of
ribosome |
|
cytosolic large ribosomal
(60S) subunit |
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
RPL35B |
|
|
protein biosynthesis |
|
structural protein of
ribosome |
|
cytosolic large ribosomal
(60S) subunit |
||
|
|
RPL35A |
|
|
protein biosynthesis |
|
structural protein of
ribosome |
|
cytosolic large ribosomal
(60S) subunit |
||
|
|
RPS20 |
|
|
protein biosynthesis |
|
structural protein of
ribosome |
|
cytosolic small ribosomal
(40S) subunit |
||
|
|
|
|
|
biological_process unknown |
|
molecular_function unknown |
|
not yet annotated |
||
|
|
RPL28 |
|
|
protein biosynthesis |
|
structural protein of
ribosome* |
|
cytosolic large ribosomal
(60S) subunit |
||
|
|
|
|
|
biological_process unknown |
|
molecular_function unknown |
|
not yet annotated |
Figure 6. Cluster from DNA microarray 6: Evolution of expression during
glucose limitation. None of these
genes appear to be induced or repressed—they share the same expression as the control. The arrestation of the cell cycle is not
selected for under glucose-limiting conditions. Figure was taken from http://genome-www4.stanford.edu/cgi-bin/SGD/expression/expressionConnection.pl.
|
Name |
|
|
Process |
|
Function |
|
|
|
cell cycle arrest |
|
cyclin-dependent protein
kinase inhibitor |
|
|
|
|
not yet annotated |
|
not yet annotated |
|
|
|
|
chromatin modeling |
|
molecular_function unknown |
|
|
|
|
biological_process unknown |
|
molecular_function unknown |
|
|
|
|
biological_process unknown |
|
molecular_function unknown |
|
|
|
|
biological_process unknown |
|
molecular_function unknown |
|
|
|
|
biological_process unknown |
|
molecular_function unknown |
|
|
|
|
biological_process unknown |
|
molecular_function unknown |
|
|
|
|
biological_process unknown |
|
molecular_function unknown |
|
|
|
|
not yet annotated |
|
molecular_function unknown |
|
|
|
|
biological_process unknown |
|
molecular_function unknown |
|
|
|
|
not yet annotated |
|
not yet annotated |
|
|
|
|
not yet annotated |
|
alpha,alpha-trehalose-phosphate
synthase (UDP-forming) |
|
|
|
|
gluconeogenesis* |
|
pyruvate carboxylase |
|
|
|
|
biological_process unknown |
|
molecular_function unknown |
|
|
|
|
not yet annotated |
|
not yet annotated |
|
|
|
|
biological_process unknown |
|
molecular_function unknown |
|
|
|
|
not yet annotated |
|
molecular_function unknown |
|
|
|
|
endocytosis* |
|
v-SNARE |
|
|
|
|
biological_process unknown |
|
protein kinase |
Figure 7. Cluster from DNA microarray 7: Expression during
sporulation. The transcription of
these genes is not very affected by sporulation. This data make sense because meiosis and spore morphogenesis take
place after the G1 phase. Figure was
taken from http://genome-www4.stanford.edu/cgi-bin/SGD/expression/expressionConnection.pl.
|
Orf |
|
Gene |
|
|
|
Process |
|
Function |
|
Component |
|
|
FAR1 |
|
|
cell cycle arrest |
|
cyclin-dependent protein
kinase inhibitor |
|
nucleus* |
||
|
|
|
|
|
biological_process unknown |
|
molecular_function unknown |
|
not yet annotated |
||
|
|
APG2 |
|
|
autophagy |
|
molecular_function unknown |
|
cellular_component unknown |
||
|
|
|
|
|
biological_process unknown |
|
molecular_function unknown |
|
not yet annotated |
||
|
|
OYE3 |
|
|
not yet annotated |
|
NADPH dehydrogenase |
|
not yet annotated |
||
|
|
|
|
|
biological_process unknown |
|
molecular_function unknown |
|
not yet annotated |
||
|
|
CCL1 |
|
|
transcription initiation,
from Pol II promoter* |
|
general RNA polymerase II
transcription factor* |
|
transcription factor TFIIH |
||
|
|
EXG2 |
|
|
not yet annotated |
|
glucan 1,3-beta-glucosidase |
|
not yet annotated |
||
|
|
|
|
|
biological_process unknown |
|
molecular_function unknown |
|
not yet annotated |
||
|
|
|
|
|
biological_process unknown |
|
molecular_function unknown |
|
not yet annotated |
||
|
|
DBP2 |
|
|
not yet annotated |
|
RNA helicase |
|
not yet annotated |
||
|
|
CHS6 |
|
|
not yet annotated |
|
not yet annotated |
|
not yet annotated |
||
|
|
|
|
|
biological_process unknown |
|
molecular_function unknown |
|
not yet annotated |
||
|
|
WSC3 |
|
|
cell wall organization and
biogenesis* |
|
molecular_function unknown |
|
membrane fraction |
YBR293W
|
This unannotated gene
(hypothetical ORF) has an unknown biological function. For more information about this gene and its
protein product see Assignment
2-My Favorite Yeast Genes: FAR1 and YBR293W.
Figure 8. Cluster from DNA microarray 1: Expression at different
alpha-factor concentrations.
YBR293W did not show any difference in expression from the control when
subjected to this mating pheromone.
This open reading frame grouped mostly with other genes that had an
unknown molecular function and biological process. Four genes did have known functions however. One gene was involved in DNA repair, another
coded for a chaperone protein used in a signal transduction pathway, a third
was involved in the stress response, and the fourth gene dealt with
transport. The biological processes
represented by the known genes did not seem to form a cohesive group. Figure was taken from http://genome-www4.stanford.edu/cgi-bin/SGD/expression/expressionConnection.pl.
|
Orf |
|
Gene |
|
|
|
Process |
|
Function |
|
Component |
|
|
|
|
|
biological_process unknown |
|
not yet annotated |
|
not yet annotated |
||
|
|
YKU70 |
|
|
DNA repair |
|
not yet annotated |
|
not yet annotated |
||
|
|
|
|
|
biological_process unknown |
|
molecular_function unknown |
|
not yet annotated |
||
|
|
ARV1 |
|
|
biological_process unknown |
|
molecular_function unknown |
|
not yet annotated |
||
|
|
|
|
|
biological_process unknown |
|
molecular_function unknown |
|
not yet annotated |
||
|
|
|
|
|
biological_process unknown |
|
molecular_function unknown |
|
not yet annotated |
||
|
|
CDC37 |
|
|
signal transduction* |
|
chaperone |
|
cellular_component unknown |
||
|
|
DSL1 |
|
|
biological_process unknown |
|
molecular_function unknown |
|
not yet annotated |
||
|
|
|
|
|
biological_process unknown |
|
molecular_function unknown |
|
not yet annotated |
||
|
|
|
|
|
biological_process unknown |
|
molecular_function unknown |
|
not yet annotated |
||
|
|
VAB2 |
|
|
not yet annotated |
|
molecular_function unknown |
|
not yet annotated |
||
|
|
|
|
|
biological_process unknown |
|
molecular_function unknown |
|
not yet annotated |
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
MAL13 |
|
|
not yet annotated |
|
not yet annotated |
|
not yet annotated |
||
|
|
|
|
|
biological_process unknown |
|
molecular_function unknown |
|
not yet annotated |
||
|
|
|
|
|
biological_process unknown |
|
molecular_function unknown |
|
not yet annotated |
||
|
|
|
|
|
biological_process unknown |
|
molecular_function unknown |
|
not yet annotated |
||
|
|
NTH1 |
|
|
stress response* |
|
alpha,alpha-trehalase |
|
cellular_component unknown |
||
|
|
|
|
|
biological_process unknown |
|
molecular_function unknown |
|
not yet annotated |
||
|
|
PMC1 |
|
|
transport |
|
not yet annotated |
|
not yet annotated |
||
|
|
|
|
|
biological_process unknown |
|
molecular_function unknown |
|
not yet annotated |
Figure 9. Cluster from DNA microarray 2: Expression in response to
alpha-factor. This grouping of genes does not seem to share very similar
expression patterns. Again, this set of
genes is primarily unannotated. A ubiquitin-specific
protease involved in deubiquitylation, a gene involved with mating, and
another related to transport were the only known genes in this cluster. However, the transport gene expression
profile does not seem to match that of YBR293W at all. Figure was taken from http://genome-www4.stanford.edu/cgi-bin/SGD/expression/expressionConnection.pl.
|
Orf |
|
Gene |
|
|
|
Process |
|
Function |
|
Component |
|
|
|
|
|
biological_process unknown |
|
not yet annotated |
|
not yet annotated |
||
|
|
|
|
|
biological_process unknown |
|
molecular_function unknown |
|
not yet annotated |
||
|
|
|
|
|
biological_process unknown |
|
molecular_function unknown |
|
not yet annotated |
||
|
|
|
|
|
biological_process unknown |
|
molecular_function unknown |
|
not yet annotated |
||
|
|
|
|
|
biological_process unknown |
|
molecular_function unknown |
|
not yet annotated |
||
|
|
|
|
|
biological_process unknown |
|
molecular_function unknown |
|
not yet annotated |
||
|
|
BTS1 |
|
|
not yet annotated |
|
not yet annotated |
|
not yet annotated |
||
|
|
|
|
|
biological_process unknown |
|
molecular_function unknown |
|
not yet annotated |
||
|
|
|
|
|
biological_process unknown |
|
molecular_function unknown |
|
not yet annotated |
||
|
|
|
|
|
biological_process unknown |
|
molecular_function unknown |
|
not yet annotated |
||
|
|
FRQ1 |
|
|
biological_process unknown |
|
calcium binding |
|
membrane |
||
|
|
|
|
|
biological_process unknown |
|
molecular_function unknown |
|
not yet annotated |
||
|
|
YUH1 |
|
|
deubiquitylation |
|
ubiquitin-specific protease |
|
cytoplasm |
||
|
|
|
|
|
biological_process unknown |
|
molecular_function unknown |
|
not yet annotated |
||
|
|
VPS35 |
|
|
not yet annotated |
|
not yet annotated |
|
not yet annotated |
||
|
|
|
|
|
biological_process unknown |
|
molecular_function unknown |
|
not yet annotated |
||
|
|
PDR12 |
|
|
not yet annotated |
|
transporter |
|
not yet annotated |
||
|
|
STE13 |
|
|
mating (sensu
Saccharomyces) |
|
not yet annotated |
|
not yet annotated |
||
|
|
RTT103 |
|
|
not yet annotated |
|
molecular_function unknown |
|
not yet annotated |
||
|
|
VCX1 |
|
|
transport |
|
not yet annotated |
|
not yet annotated |
||
|
|
|
|
|
biological_process unknown |
|
molecular_function unknown |
|
not yet annotated |
Figure 10. Cluster from DNA microarray 3: Expression in response to
DNA-damaging agents. YBR293W was not induced nor was it
repressed when yeast was subjected to these mutagens. This ORF did not cluster with any other genes. Figure was taken from http://genome-www4.stanford.edu/cgi-bin/SGD/expression/expressionConnection.pl.
|
Orf |
|
Gene |
|
|
|
Process |
|
Function |
|
Component |
|
|
|
|
|
biological_process unknown |
|
not yet annotated |
|
not yet annotated |
Figure 11. Cluster from DNA microarray 4: Expression during the cell
cycle. YBR293W does not cluster with any
other known ORFS. The expression of
this ORF does not seem to change over the course of the yeast’s cell
cycle. There are a lot of unknown data
point (grey). Figure was taken from http://genome-www4.stanford.edu/cgi-bin/SGD/expression/expressionConnection.pl.
|
Name |
Score |
Peak |
|
|
0.08 |
|
|
|
|
Reference Genes |
|
||
|
10.9 |
G1 |
|
|
|
10.68 |
S |
|
|
|
3.08 |
G2 |
|
|
|
6.726 |
M |
|
|
|
11.8 |
M/G1 |
|
|
Note: We only generated a list of genes with similar patterns of expression for genes whose "aggregate CDC scores" were in the top 1200 (Score >= 0.95). YBR293W did not have a score high enough for us to
generate such a list.
Figure 12. Cluster from DNA microarray 5: Expression during the diauxic
shift. For the most part, a shift
from an aerobic environment to an anaerobic one did not affect the
transcription of these genes. Figure
was taken from http://genome-www4.stanford.edu/cgi-bin/SGD/expression/expressionConnection.pl.
|
Orf |
|
Gene |
|
|
|
Process |
|
Function |
|
Component |
|
|
|
|
|
biological_process unknown |
|
not yet annotated |
|
not yet annotated |
||
|
|
|
|
|
biological_process unknown |
|
molecular_function unknown |
|
not yet annotated |
||
|
|
|
|
|
biological_process unknown |
|
molecular_function unknown |
|
not yet annotated |
||
|
|
|
|
|
biological_process unknown |
|
molecular_function unknown |
|
not yet annotated |
||
|
|
|
|
|
biological_process unknown |
|
molecular_function unknown |
|
not yet annotated |
||
|
|
MUD1 |
|
|
mRNA splicing |
|
not yet annotated |
|
not yet annotated |
||
|
|
MSB3 |
|
|
actin filament organization* |
|
RAB GTPase activator |
|
bud tip* |
||
|
|
|
|
|
biological_process unknown |
|
molecular_function unknown |
|
not yet annotated |
||
|
|
DCI1 |
|
|
fatty acid beta-oxidation |
|
dodecenoyl-CoA
delta-isomerase |
|
peroxisomal matrix |
||
|
|
PRP4 |
|
|
not yet annotated |
|
not yet annotated |
|
not yet annotated |
||
|
|
MUP3 |
|
|
transport |
|
not yet annotated |
|
not yet annotated |
||
|
|
|
|
|
biological_process unknown |
|
molecular_function unknown |
|
not yet annotated |
||
|
|
TFC6 |
|
|
transcription initiation, from
Pol III promoter |
|
RNA polymerase III
transcription factor |
|
transcription factor TFIIIC |
||
|
|
|
|
|
biological_process unknown |
|
molecular_function unknown |
|
not yet annotated |
||
|
|
GAL10 |
|
|
galactose metabolism |
|
UDP-glucose 4-epimerase |
|
cytoplasm |
||
|
|
MTL1 |
|
|
not yet annotated |
|
molecular_function unknown |
|
not yet annotated |
||
|
|
VPS28 |
|
|
not yet annotated |
|
not yet annotated |
|
not yet annotated |
||
|
|
SPO12 |
|
|
meiosis I |
|
molecular_function unknown |
|
nucleus |
||
|
|
|
|
|
biological_process unknown |
|
molecular_function unknown |
|
not yet annotated |
||
|
|
OCT1 |
|
|
iron homeostasis* |
|
metallopeptidase |
|
mitochondrion |
||
|
|
|
|
|
biological_process unknown |
|
molecular_function unknown |
|
not yet annotated |
Figure 13. Cluster from DNA microarray 6: Evolution of expression during
glucose limitation. YBR293W once again did not display
a difference in transcription from the control. This ORF is not likely selected for as glucose becomes
increasingly limiting. Most of the ORFs
in this set are of unknown process and function. However, some of the known genes are involved in a stress
response, transport, and a signal transduction pathway related to mating
signalling. Figure was taken from http://genome-www4.stanford.edu/cgi-bin/SGD/expression/expressionConnection.pl.
|
Name |
|
|
Process |
|
Function |
|
|
|
biological_process unknown |
|
not yet annotated |
|
|
|
|
not yet annotated |
|
molecular_function unknown |
|
|
|
|
biological_process unknown |
|
molecular_function unknown |
|
|
|
|
not yet annotated |
|
molecular_function unknown |
|
|
|
|
biological_process unknown |
|
molecular_function unknown |
|
|
|
|
biological_process unknown |
|
molecular_function unknown |
|
|
|
|
biological_process unknown |
|
molecular_function unknown |
|
|
|
|
biological_process unknown |
|
molecular_function unknown |
|
|
|
|
biological_process unknown |
|
molecular_function unknown |
|
|
|
|
stress response* |
|
heat shock protein |
|
|
|
|
biological_process unknown |
|
molecular_function unknown |
|
|
|
|
biological_process unknown |
|
molecular_function unknown |
|
|
|
|
biological_process unknown |
|
molecular_function unknown |
|
|
|
|
biological_process unknown |
|
molecular_function unknown |
|
|
|
|
biological_process unknown |
|
molecular_function unknown |
|
|
|
|
biological_process unknown |
|
molecular_function unknown |
|
|
|
|
transport |
|
not yet annotated |
|
|
|
|
signal transduction of
mating signal (sensu Saccharomyces) |
|
heterotrimeric G-protein
GTPase, alpha subunit |
|
|
|
|
biological_process unknown |
|
molecular_function unknown |
|
|
|
|
biological_process unknown |
|
molecular_function unknown |
|
|
|
|
biological_process unknown |
|
molecular_function unknown |
Figure 14. Cluster from DNA microarray 7: Expression during
sporulation. YBR293W exhibits induction around
0.5 hours and then repression beginning around 5 hours. This repression lasts throughout the rest of
the time observed and becomes increasingly greater. The other genes in this cluster share a very similar expression
profile. However, the majority of these
genes are of unknown biological process and molecular function. The known genes are involved with phospholipid
metabolism, the tricarboxylic acid cycle, vacuolar protein degradation,
fumarate transport, protein folding, and protein biosynthesis. YBR293W could possibly be involved in meoisis or spore
morphogenesis. Figure was taken from http://genome-www4.stanford.edu/cgi-bin/SGD/expression/expressionConnection.pl.
|
Orf |
|
Gene |
|
|
|
Process |
|
Function |
|
Component |
|
|
|
|
|
biological_process unknown |
|
not yet annotated |
|
not yet annotated |
||
|
|
HAT1 |
|
|
not yet annotated |
|
not yet annotated |
|
not yet annotated |
||
|
|
|
|
|
biological_process unknown |
|
molecular_function unknown |
|
not yet annotated |
||
|
|
LAP4 |
|
|
vacuolar protein degradation |
|
vacuolar aminopeptidase I |
|
vacuole |
||
|
|
|
|
|
biological_process unknown |
|
molecular_function unknown |
|
not yet annotated |
||
|
|
SFC1 |
|
|
fumarate transport* |
|
succinate/fumarate
antiporter |
|
mitochondrial inner
membrane |
||
|
|
GSF2 |
|
|
not yet annotated |
|
molecular_function unknown |
|
not yet annotated |
||
|
|
NCE103 |
|
|
not yet annotated |
|
molecular_function unknown |
|
not yet annotated |
||
|
|
|
|
|
biological_process unknown |
|
molecular_function unknown |
|
not yet annotated |
||
|
|
FUN34 |
|
|
biological_process unknown |
|
molecular_function unknown |
|
not yet annotated |
||
|
|
|
|
|
biological_process unknown |
|
molecular_function unknown |
|
not yet annotated |
||
|
|
|
|
|
biological_process unknown |
|
molecular_function unknown |
|
cellular_component unknown |
||
|
|
|
|
|
biological_process unknown |
|
molecular_function unknown |
|
not yet annotated |
||
|
|
|
|
|
biological_process unknown |
|
molecular_function unknown |
|
not yet annotated |
||
|
|
|
|
|
biological_process unknown |
|
molecular_function unknown |
|
not yet annotated |
||
|
|
|
|
|
biological_process unknown |
|
molecular_function unknown |
|
not yet annotated |
||
|
|
DPL1 |
|
|
phospholipid metabolism |
|
not yet annotated |
|
not yet annotated |
||
|
|
CCT6 |
|
|
protein folding* |
|
chaperone |
|
cytoplasm* |
||
|
|
IDH2 |
|
|
tricarboxylic acid cycle* |
|
isocitrate dehydrogenase
(NAD+) |
|
mitochondrial matrix |
||
|
|
PPH21 |
|
|
protein biosynthesis* |
|
protein phosphatase type 2A |
|
protein phosphatase type 2A |
||
|
|
CYB2 |
|
|
not yet annotated |
|
L-lactate dehydrogenase
(cytochrome) |
|
not yet annotated |
Conclusions
YBR293W clustered with transport
(PMC1 and SSY1), stress response (NTH1 and SSA3), and signal transduction (GPA1
and CDC37) genes twice out of seven DNA microarrays. I would propose that YBR293W is part of a responsive pathway that
functions to protect the yeast in some capacity. I really had no leads from the last web assignment. I proposed that this ORF was involved with budding. However, this ORF only clusters with a
transcription initiation factor or a gene involved in meiosis one time. But, this ORF is induced and then repressed
during the sporulation experiment, so a function with budding is still a
possibility. This ORF is probably not
involved in respiration or metabolism though since its expression was not
affected by those experiments.
References
Butty
AC, et al.1998. The Role of Far1p in linking the heterotrimeric G
protein to polarity establishment proteins during yeast
mating. Science 282:1511-1516.
DeRisi
JL, Iyer VR, Brown PO. Exploring the Metabolic and Genetic Control of Gene
Expression on a Genomic Scale.
http://cmgm.stanford.edu/pbrown/explore/.
Ferea
T, Botstein D, Brown PO, Rosenzweig RF. 1999. Systematic Changes in Gene
Expression Patterns Following
Adaptive Evolution in Yeast. PNAS 96:
9721-9726.
Gasch
AP et al. 2001. Genomic Expression Responses to DNA-damaging Agents and
the Regulatory Role of the Yeast ATR
Homolog Mec1p. Molecular Biology of the
Cell 12: 2987-3003.
Gasch
AP et al. 2000. Genomic Expression Programs in the Response of Yeast
Cells to Environmental Changes.
Molecular
Biology of the Cell 11: 4241-4257.
Peter M, Herskowitz I.
1994. Direct Inhibition of the Yeast Cyclin-Dependent Kinase Cdc28-Cln by Far1.
Science 265: 1228-1231.
Roberts CJ et al.
2000. Signaling and Circuitry of Multiple MAPK Pathways Revealed by a Matrix of
Global Gene
Expression
Profiles. Science 287: 873-880.
SGD database. 2001.Stanford. http://genome-www4.stanford.edu/cgi-bin/SGD/expression/expressionConnection.pl
Spellman
et al. 1998. Comprehensive Identification of Cell
Cycle-regulated Genes of the Yeast Saccharomyces
cerevisiae by Microarray
Hybridization. Molecular Biology of the Cell 9: 3273-3297.
http://cmgm.stanford.edu/pbrown/sporulation/index.html
http://staffa.wi.mit.edu/young_public/chromatin/histones.html