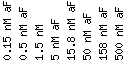What do microarray
experiments tell us about my favorite annotated and unannotated yeast gene?
This page was produced as an assignment for an undergraduate course at
Davidson College.
Purpose
The
purpose of this page is to explore how our annotated and unannotated genes are
expressd by using microarray data. Our
ultimate mission is to try and decipher what possible roles our two genes may
play based on the microarray expression data.
Experiments that have been performed using microarray technology and will be used to examine my two genes
1-Expression response to increasing alpha factor concentration (alpha factor is a mating pheromone)
2-Expression response to alpha factor over time
3-Expression response during a diauxic shift
A diauxic shift is when cells continue to divide as glucose concentration decreases.
4-Expression during the cell cycle
5-Expression during sporulation
6-Expression during histone depletion
The histone depleted was one found in nucleosomes.
7-Expression during
environmental changes
8-Expression in wildtype and mec1 mutants when subjected to damaging agents
Mec1 is a gene involved in a damage signaling pathway. Mec1 was deleted in mec1 mutatnts.
All figures will use the following scale:
Scale : (fold repression/induction)
![]()
SGS1-My annotated yeast gene
As was explained in the second web site, SGS1 codes for a DNA helicase. Frei et al. (1999) propose that SGS1 interacts with RNA polymerase II during rRNA transcription. McVey et al. (2001) suggest that SGS1 also plays a role in the cell cycle at the G1 stage and the G2/M checkpoint. Yamagata et al. (1998) suggest that SGS 1 prevents chromosome missegregation.
In microarray experiments SGS1 often clusters with gene for RNA Polymerase transcription factors, genes involved in chromosome segregation, and genes involved in cell cycle checkpoints.
A Look At the Data
Figure 1 Genes that had similar expression patterns when compared to SGS1 during a diauxic shift
|
Orf |
|
Gene |
|
|
|
Process |
|
Function |
|
Component |
|
|
SGS1 |
|
|
not yet annotated |
|
not yet annotated |
|
not yet annotated |
||
|
|
SRB5 |
|
|
transcription, from Pol II
promoter |
|
RNA polymerase II
transcription mediator |
|
mediator complex |
||
|
|
|
|
|
biological_process unknown |
|
molecular_function unknown |
|
not yet annotated |
||
|
|
|
|
|
biological_process unknown |
|
molecular_function unknown |
|
not yet annotated |
||
|
|
DNF3 |
|
|
biological_process unknown |
|
molecular_function unknown |
|
not yet annotated |
||
|
|
|
|
|
biological_process unknown |
|
molecular_function unknown |
|
not yet annotated |
||
|
|
SSK22 |
|
|
protein amino acid
phosphorylation* |
|
MAP kinase kinase kinase |
|
cellular_component unknown |
||
|
|
SPC42 |
|
|
microtubule nucleation* |
|
structural protein of
cytoskeleton |
|
outer plaque of spindle
pole body* |
||
|
|
RPA135 |
|
|
transcription, from Pol I
promoter |
|
DNA-directed RNA polymerase
I |
|
DNA-directed RNA polymerase
I |
||
|
|
|
|
|
biological_process unknown |
|
molecular_function unknown |
|
not yet annotated |
||
|
|
ACE2 |
|
|
G1-specific transcription
in mitotic cell cycle |
|
transcriptional activator |
|
nucleus* |
||
|
|
REV3 |
|
|
DNA repair* |
|
zeta DNA polymerase |
|
nucleus |
||
|
|
|
|
|
biological_process unknown |
|
molecular_function unknown |
|
not yet annotated |
||
|
|
|
|
|
biological_process unknown |
|
molecular_function unknown |
|
not yet annotated |
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
ESP1 |
|
|
not yet annotated |
|
not yet annotated |
|
not yet annotated |
||
|
|
RRP3 |
|
|
mRNA splicing* |
|
ATP dependent RNA helicase |
|
nucleolus |
||
|
|
|
|
|
biological_process unknown |
|
molecular_function unknown |
|
not yet annotated |
||
|
|
|
|
|
biological_process unknown |
|
molecular_function unknown |
|
not yet annotated |
||
|
|
INP53 |
|
|
not yet annotated |
|
inositol-1,4,5-triphosphate
5-phosphatase |
|
not yet annotated |
||
|
|
|
|
|
biological_process unknown |
|
molecular_function unknown |
|
not yet annotated |
Table taken from SGD Expression Connection data base at the
the following link:
http://genome-www4.stanford.edu/cgi-bin/SGD/expression/expressionConnection.pl?query=SGS1&noSearch=1
During a diauxic shift SGS1 was repressed. SGS1 clustered with SRB5, a RNA Pol II transcription mediator, and ACE2, a G1-specific transcription activator. These support the findings that SGS1 is involved in RNA polymerase II transcription and is active in the G1 cell cycle stage.
Figure 2 Genes that had similar expression patterns to SGS1 at different alpha-factor concentrations
|
Orf |
|
Gene |
|
|
|
Process |
|
Function |
|
Component |
|
|
SGS1 |
|
|
not yet annotated |
|
not yet annotated |
|
not yet annotated |
||
|
|
|
|
|
biological_process unknown |
|
molecular_function unknown |
|
not yet annotated |
||
|
|
SNU56 |
|
|
mRNA splicing |
|
not yet annotated |
|
not yet annotated |
||
|
|
SER3 |
|
|
serine biosynthesis |
|
phosphoglycerate
dehydrogenase |
|
cellular_component unknown |
||
|
|
|
|
|
biological_process unknown |
|
molecular_function unknown |
|
not yet annotated |
||
|
|
|
|
|
biological_process unknown |
|
molecular_function unknown |
|
not yet annotated |
||
|
|
|
|
|
biological_process unknown |
|
molecular_function unknown |
|
not yet annotated |
||
|
|
FIN1 |
|
|
not yet annotated |
|
not yet annotated |
|
not yet annotated |
||
|
|
CDC1 |
|
|
mating (sensu Saccharomyces)* |
|
molecular_function unknown |
|
cell |
||
|
|
USO1 |
|
|
not yet annotated |
|
not yet annotated |
|
not yet annotated |
||
|
|
CSR1 |
|
|
cell wall organization and
biogenesis |
|
molecular_function unknown |
|
cellular_component unknown |
||
|
|
TUB1 |
|
|
mitotic chromosome segregation* |
|
structural protein of
cytoskeleton |
|
spindle pole body* |
||
|
|
FEN1 |
|
|
fatty acid biosynthesis* |
|
molecular_function unknown |
|
endoplasmic reticulum
membrane |
||
|
|
SCO1 |
|
|
protein complex assembly* |
|
molecular_function unknown |
|
mitochondrial inner
membrane |
||
|
|
SPC19 |
|
|
microtubule nucleation |
|
structural protein of
cytoskeleton |
|
spindle pole body |
||
|
|
TUB2 |
|
|
mitotic chromosome segregation* |
|
structural protein of
cytoskeleton |
|
spindle pole body* |
||
|
|
CLB1 |
|
|
regulation of CDK activity* |
|
G2/M-specific cyclin |
|
cellular_component unknown |
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
TAF60 |
|
|
transcription initiation,
from Pol II promoter* |
|
general RNA polymerase II
transcription factor |
|
TFIID complex* |
||
|
|
|
|
|
biological_process unknown |
|
molecular_function unknown |
|
not yet annotated |
||
|
|
SWI5 |
|
|
G1-specific transcription
in mitotic cell cycle |
|
transcriptional activator |
|
nucleus* |
Table taken from SGD Expression Connection data base at the
the following link:
http://genome-www4.stanford.edu/cgi-bin/SGD/expression/expressionConnection.pl?query=SGS1&noSearch=1
SGS1 was slightly repressed as alpha concentration reached a concentration of 5-15.8 nm. Then expression reuturned to a no change condition as the concentration continued to increase. The above table shows that SGS1 clustered with TAF60, a Pol II transcription factor and with SWI5, a G1 specific transcriptional activator. SGS1 also clustered with TUB1 and TUB2, which are both involved in chromosome segregation, and CLB1, which is involved in the cell cylce G2/M checkpoint. These findings also support the hypothesis proposed by Frei, McVey, and Yagamata that SGS1 is involved in rRNA transcription and cell division.
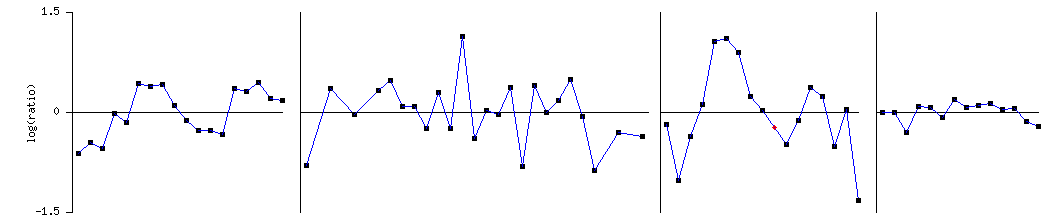
Figure 3 SGS1 expression during various phases of the cell cylce
|
Name |
Score |
Peak |
|
|
0.923 |
|
|
|
|
Reference Genes |
|
||
|
10.9 |
G1 |
|
|
|
10.68 |
S |
|
|
|
3.08 |
G2 |
|
|
|
6.726 |
M |
|
|
|
11.8 |
M/G1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Plot of SGS1 (YMR190C) |
|
||
Table taken from SGD Expression Connection
data base at the the following link:
http://genome-www4.stanford.edu/cgi-bin/SGD/expression/expressionConnection.pl?query=SGS1&noSearch=1
This microarray
data set indicate that SGS1 in repressed and induced at varying points in the
cell cycle. This supports the
hypothesis that SGS1 is involved in cell cycle checkpoints. However SGS1 did not have a high enough
score for the database to cluster it with genes expressing similar patterns
during the cell cylce. This is
interesting since SGS1 is believed to play a role in the cell cycle.
Figure 4 Genes that clustered with SGS1 during histone depletion
|
Orf |
|
Gene |
|
|
|
Process |
|
Function |
|
Component |
|
|
SGS1 |
|
|
not yet annotated |
|
not yet annotated |
|
not yet annotated |
||
|
|
|
|
|
biological_process unknown |
|
molecular_function unknown |
|
not yet annotated |
||
|
|
|
|
|
biological_process unknown |
|
molecular_function unknown |
|
not yet annotated |
||
|
|
DAL7 |
|
|
allantoin catabolism |
|
malate synthase |
|
peroxisomal matrix |
||
|
|
|
|
|
biological_process unknown |
|
molecular_function unknown |
|
not yet annotated |
||
|
|
|
|
|
biological_process unknown |
|
molecular_function unknown |
|
not yet annotated |
||
|
|
|
|
|
biological_process unknown |
|
molecular_function unknown |
|
not yet annotated |
||
|
|
|
|
|
biological_process unknown |
|
molecular_function unknown |
|
not yet annotated |
||
|
|
GAT2 |
|
|
not yet annotated |
|
not yet annotated |
|
not yet annotated |
||
|
|
|
|
|
biological_process unknown |
|
molecular_function unknown |
|
not yet annotated |
||
|
|
|
|
|
biological_process unknown |
|
molecular_function unknown |
|
not yet annotated |
||
|
|
|
|
|
biological_process unknown |
|
molecular_function unknown |
|
not yet annotated |
||
|
|
POM152 |
|
|
mRNA-nucleus export* |
|
structural protein |
|
nuclear pore* |
||
|
|
PLB2 |
|
|
not yet annotated |
|
Lysophospholipase |
|
not yet annotated |
||
|
|
SNF11 |
|
|
chromatin modeling |
|
non-specific RNA polymerase
II transcription factor |
|
nucleosome remodeling
complex |
||
|
|
|
|
|
biological_process unknown |
|
molecular_function unknown |
|
not yet annotated |
||
|
|
SDS3 |
|
|
not yet annotated |
|
not yet annotated |
|
not yet annotated |
||
|
|
|
|
|
biological_process unknown |
|
molecular_function unknown |
|
not yet annotated |
||
|
|
PGS1 |
|
|
not yet annotated |
|
CDP-diacylglycerol-serine
O-phosphatidyltransferase |
|
not yet annotated |
||
|
|
PEX10 |
|
|
peroxisome organization and
biogenesis |
|
molecular_function unknown |
|
cellular_component unknown |
||
|
|
|
|
|
biological_process unknown |
|
molecular_function unknown |
|
not yet annotated |
Table taken from SGD Expression Connection data base at the
the following link:
http://genome-www4.stanford.edu/cgi-bin/SGD/expression/expressionConnection.pl?query=SGS1&noSearch=1
SGS1 was first
repressed at time 0 and then was induced after 2-4 hours of histone
depletion. The histone depleted in this
experiment is found in the nucleosomes.
This suggests that SGS1 is somehow regulated by the deletion of histones
found in nucleosomes.
Putting it all together
SGS1 seems to cluster with transcription factors that regulate the cell cycle, specifically SWI5 and ACE2. However when SGS1 was compared to the cell cycle microarray data, it did not score a high enough score to be clustered with other genes that were determined to regulate the cell cycle. These seem to be two contradictory reports that should be explored further. Perhaps SGS1 does not elicit a response that reaches the threshold set in the cell cycle experiment. SGS1 also clustered with polymerase II transcription factors. This supports the current hypothesis that SGS1 is involved in rRNA transcription. For more detailed infor on SGS1’s role in the cell go my second web site.
UNANNOTATED YEAST GENE YJU3
In the second web site, it was suggested that YJU3 may be a abhydrolase protein and a phospholipase protein. In microarray experiments YJU3 is often clustered with genes that code for hydrolases, oxidoreductases, transport functions, and protein synthesis or modification.
Microarray Data
Figure 5 Genes that showed similar expression patterns to YJU3 during a diauxic shift
|
Orf |
|
Gene |
|
|
|
Process |
|
Function |
|
Component |
|
|
YJU3 |
|
|
biological_process unknown |
|
molecular_function unknown |
|
Not yet annotated |
||
|
|
SEC17 |
|
|
Vesicular
transport,activator** |
|
not yet annotated |
|
Not yet annotated |
||
|
|
|
|
|
biological_process unknown |
|
molecular_function unknown |
|
Cellular_component unknown |
||
|
|
|
|
|
biological_process unknown |
|
molecular_function unknown |
|
not yet annotated |
||
|
|
|
|
|
biological_process unknown |
|
molecular_function unknown |
|
not yet annotated |
||
|
|
GLO2 |
|
|
carbohydrate metabolism |
|
Hydroxyacylglutathione
hydrolase |
|
cytoplasm |
||
|
|
CPR6 |
|
|
protein folding |
|
peptidylprolyl isomerase |
|
cytoplasm |
||
|
|
|
|
|
biological_process unknown |
|
molecular_function unknown |
|
not yet annotated |
||
|
|
|
|
|
Oxidoreductase** |
|
not yet annotated |
|
not yet annotated |
||
|
|
ALD2 |
|
|
amino acid and derivative
metabolism |
|
aldehyde dehydrogenase |
|
cytoplasm |
||
|
|
GRX1 |
|
|
oxidative stress response |
|
Glutaredoxin |
|
Cellular_component unknown |
||
|
|
NVJ1 |
|
|
not yet annotated |
|
molecular_function unknown |
|
not yet annotated |
||
|
|
|
|
|
biological_process unknown |
|
molecular_function unknown |
|
not yet annotated |
||
|
|
SUC2 |
|
|
sucrose catabolism |
|
beta-fructofuranosidase |
|
not yet annotated |
||
|
|
NYV1 |
|
|
non-selective vesicle
fusion |
|
v-SNARE |
|
vacuolar membrane |
||
|
|
|
|
|
biological_process unknown |
|
molecular_function unknown |
|
not yet annotated |
||
|
|
|
|
|
biological_process unknown |
|
molecular_function unknown |
|
not yet annotated |
||
|
|
CPR2 |
|
|
stress response |
|
peptidylprolyl isomerase |
|
Cellular_component unknown |
||
|
|
|
|
|
biological_process unknown |
|
molecular_function unknown |
|
not yet annotated |
||
|
|
GLC8 |
|
|
not yet annotated |
|
molecular_function unknown |
|
not yet annotated |
||
|
|
DDR48 |
|
|
DNA repair |
|
molecular_function unknown |
|
Cellular_component unknown |
This table has been modified from its original version.
** indicate that the YPD gave a function for the corresponding gene that was not originally in the table.
Table taken from SGD Expression Connection data base at the the following link: http://genome-www4.stanford.edu/cgi-bin/SGD/expression/expressionConnection.pl?query=YJU3&noSearch=1
During the diauxic shift YJU3 expression was induced. This suggests that YJU3 may be involved in cell stress since it is not induced until glucose is almost depleted. YJU3 clustered with hydrolases involved in carbohoydrate metabolism, genes involved in vesicular transport, protein folding, and oxidoreductases involved in amino acid metabolism and cell stress.
Figure 6 Genes that showed similar expression patterns to YJU3 to added alapa factor over time
|
Orf |
|
Gene |
|
|
|
Process |
|
Function |
|
Component |
|
|
YJU3 |
|
|
biological_process unknown |
|
molecular_function unknown |
|
not yet annotated |
||
|
|
SNZ2 |
|
|
biological_process unknown |
|
molecular_function unknown |
|
not yet annotated |
||
|
|
DAL3 |
|
|
not yet annotated |
|
ureidoglycolate hydrolase |
|
not yet annotated |
||
|
|
KAR2 |
|
|
protein folding* |
|
adenosinetriphosphatase* |
|
endoplasmic reticulum lumen |
||
|
|
PRM7 |
|
|
mating (sensu
Saccharomyces) |
|
molecular_function unknown |
|
integral membrane protein |
||
|
|
YHC3 |
|
|
Transporter** |
|
molecular_function unknown |
|
not yet annotated |
||
|
|
SNQ2 |
|
|
Hydrolase; active
transporter** |
|
not yet annotated |
|
not yet annotated |
||
|
|
RIM15 |
|
|
Meiosis |
|
protein kinase |
|
not yet annotated |
||
|
|
|
|
|
biological_process unknown |
|
molecular_function unknown |
|
not yet annotated |
||
|
|
|
|
|
biological_process unknown |
|
molecular_function unknown |
|
not yet annotated |
||
|
|
|
|
|
biological_process unknown |
|
molecular_function unknown |
|
not yet annotated |
||
|
|
PGS1 |
|
|
not yet annotated |
|
CDP-diacylglycerol-serine
O-phosphatidyltransferase |
|
not yet annotated |
||
|
|
YHM1 |
|
|
Transport |
|
not yet annotated |
|
not yet annotated |
||
|
|
|
|
|
biological_process unknown |
|
molecular_function unknown |
|
not yet annotated |
||
|
|
PDR5 |
|
|
Hydrolase** |
|
Transporter |
|
not yet annotated |
||
|
|
TPO4 |
|
|
Active transporter** |
|
molecular_function unknown* |
|
vacuolar membrane |
||
|
|
|
|
|
biological_process unknown |
|
molecular_function unknown |
|
not yet annotated |
||
|
|
|
|
|
Polymerase II transcription
factor** |
|
molecular_function unknown |
|
not yet annotated |
||
|
|
ECM40 |
|
|
cell wall organization and
biogenesis* |
|
amino acid
N-acetyltransferase* |
|
mitochondrial matrix |
||
|
|
DNM1 |
|
|
mitochondrion organization
and biogenesis |
|
GTPase |
|
mitochondrion |
||
|
|
|
|
|
Protein synthesis; translation
factor** |
|
molecular_function unknown |
|
not yet annotated |
This table has been modified from its original version.
** indicate that the YPD gave a function for the corresponding gene that was not originally in the table.
Table taken from SGD Expression Connection data base at the the following link: http://genome-www4.stanford.edu/cgi-bin/SGD/expression/expressionConnection.pl?query=YJU3&noSearch=1
There appears to be no apparent change as alpha concentration increases. YJU3 does cluster with hydrolases and transporters, and genes involved in protein synthesis.
Figure 7 Genes that showed similar expression patterns to
YJU3 during sporulation
|
Orf |
|
Gene |
|
|
|
Process |
|
Function |
|
Component |
|
|
YJU3 |
|
|
Biological_process unknown |
|
molecular_function unknown |
|
not yet annotated |
||
|
|
FLO9 |
|
|
Flocculation |
|
Not yet annotated |
|
not yet annotated |
||
|
|
|
|
|
Biological_process unknown |
|
molecular_function unknown |
|
not yet annotated |
||
|
|
|
|
|
Biological_process unknown |
|
molecular_function unknown |
|
not yet annotated |
||
|
|
UBA3 |
|
|
ubiquitin cycle |
|
ubiquitin activating enzyme |
|
cellular_component unknown |
||
|
|
IES1 |
|
|
Biological_process unknown |
|
molecular_function unknown |
|
not yet annotated |
||
|
|
|
|
|
Biological_process unknown |
|
molecular_function unknown |
|
not yet annotated |
||
|
|
UBI4 |
|
|
stress response* |
|
protein degradation tagging |
|
cytoplasm |
||
|
|
CAT8 |
|
|
Gluconeogenesis |
|
transcription factor |
|
not yet annotated |
||
|
|
IXR1 |
|
|
Pol II transcription
factor** |
|
Transcription inhibitor or
repressor** |
|
not yet annotated |
||
|
|
SER1 |
|
|
Not yet annotated |
|
phosphoserine
aminotransferase |
|
not yet annotated |
||
|
|
|
|
|
Biological_process unknown |
|
molecular_function unknown |
|
not yet annotated |
||
|
|
MRPL38 |
|
|
protein biosynthesis |
|
structural protein of
ribosome |
|
mitochondrial large
ribosomal subunit |
||
|
|
|
|
|
Biological_process unknown |
|
molecular_function unknown |
|
not yet annotated |
||
|
|
SCO2 |
|
|
copper ion transport |
|
molecular_function unknown |
|
mitochondrial membrane |
||
|
|
CIC1 |
|
|
Biological_process unknown |
|
molecular_function unknown |
|
cellular_component unknown |
||
|
|
BIO5 |
|
|
biotin biosynthesis |
|
Not yet annotated |
|
not yet annotated |
||
|
|
UGA2 |
|
|
oxidative stress response* |
|
succinate-semialdehyde
dehydrogenase (NAD(P)+) |
|
cellular_component unknown |
||
|
|
|
|
|
Biological_process unknown |
|
molecular_function unknown |
|
not yet annotated |
||
|
|
|
|
|
Biological_process unknown |
|
molecular_function unknown |
|
not yet annotated |
||
|
|
PPM1 |
|
|
protein modification |
|
Not yet annotated |
|
not yet annotated |
This table has been modified from its original version.
** indicate that the YPD gave a function for the corresponding gene that was not originally in the table.
Table taken from SGD Expression Connection data base at the the following link: http://genome-www4.stanford.edu/cgi-bin/SGD/expression/expressionConnection.pl?query=YJU3&noSearch=1
The YJU3 gene is repressed during sporulation. YJU3 has clustered with many genes of unknown function. This may indicate that YJU3 plays a role in a pathway that is not very well understood yet. YJU3 did cluster with CAT18 a gene involved in protein modification and gluconogenesis.
Figure 8 Genes that clustered with YJU3 during cell cycle experiments
|
Name |
Score |
Peak |
|
|
1.126 |
|
|
|
|
1.038 |
|
|
|
|
0.987 |
|
|
|
|
1.352 |
G2 |
|
|
|
2.42 |
G2 |
|
|
|
1.279 |
|
|
|
|
2.672 |
S |
|
|
|
3.08 |
G2 |
|
|
|
4.41 |
G2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Plot of YJU3 (YKL094W) |
|
||
Figure taken by following links from the following SGD website: http://genome-www4.stanford.edu/cgi-bin/SGD/expression/expressionConnection.pl?query=YJU3&noSearch=1
YJU3 did have a high enough score to cluster with other genes involved in the cell cycle. It seems that YJU3 is slightly induced and then repressed in the cdc15 and cdc 28 experiments.
Figure 9 YJU3 expression when subjected to damaging agents
|
|
|
Gene |
|
|
|
Process |
|
Function |
|
Component |
|
|
YJU3 |
|
|
biological_process unknown |
|
molecular_function unknown |
|
not yet annotated |
Figure taken by following links from the following SGD website: http://genome-www4.stanford.edu/cgi-bin/SGD/expression/expressionConnection.pl?query=YJU3&noSearch=1
YJU3 was induced in both wild type cells and mec1 mutants when subjected to radiation and heat shock. YJU3 was not induced when subjected to MMS. This again suggests that YJU3 is involved in cell stress responses. However it does not seem to be regulated by the mec1 damage signaling pathway.
Environmental changes
YJU3 was induced when it was subjected to heat shock, to H202, and to diamide. This suggests that it might be involved in stress coping mechanisms. To view the figure of data for the expression of YJU3 during varying environmental conditions go to the following link: http://genome-www4.stanford.edu/cgi-bin/SGD/expression/expressionConnection.pl?query=YJU3&noSearch=1
Putting it all together for YJU3
YJU3 seems to somehow be involved with the cell cycle. YJU3 also clusters with hydrolases, transporters and genes involved in protein synthesis and modification. YJU3 is induced when glusoce levels are low and YJU3 also clustered with CAT8 a transcriptional regulator of gluconogenesis. Thus, perhaps YJU3 is involved in a metabolic pathway that operates under low glusoce conditions. Furthermore, the data suggest that YJU3 is not just involved in glucose depletion stress response but also in other stress repsonse mechanisms. YJU3 is induced when subjected to heat shock, radiation, H202, diamide, and MMS. This would also explain why YJU3 often clustered with oxidoreductases and genes involved in cell stress mechanisms.
References
Frei, Christian and Susan M. Gasser. January 2000. The yeast
Sgs1p helicase acts upstream of
Rad53p in the DNA replication checkpoint and colocalizes
with Rad53p in S-phase-specific
foci. Genes and Dev. 14(1): 81-96.http://www.genesdev.org/cgi/content/full/14/1/81
McVey, M. , Kaeberlein, M. , Tissenbaum, H. A. &
Guarente, L. 2001. The short life span of
Saccharomyces servisiae sgs1 and srs2 mutants is a composite
of normal aging processes and
mitotic arrest due to defective recombination. Genetics
157: 1531-1542.
http://www.genetics.org/cgi/content/full/157/4/1531
SGD database. 2001.Stanford.
http://genome-www4.stanford.edu/cgi-bin/SGD/expression/expressionConnection.pl
Yamagata K, Kato J, Shimamoto A, Goto M, Furuichi Y, Ikeda
H. July 1998. Bloom's and
Werner's syndrome genes suppress hyperrecombination in yeast
sgs1 mutant: implication for
genomic instability in human diseases. PNAS (U S A) 95(15):8733-8.
http://www.pnas.org/cgi/content/full/95/15/8733
YPD database. 2001. Proteome, Inc.
http://www.proteome.com/databases/YPD/reports/YJU3.html
Comments and suggestions: mailto:lirobinson@davidson.edu