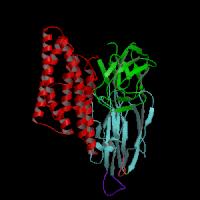
Bt Toxin Protein Structure
permission pending from P. Grochulski Homepage
Environmental Disturbance
What are Bt toxins?
Bt toxins are crystal proteins from the bacteria Bacillus thuringiensis. Bt produces proteins that aggregate to form a crystal. The crystal proteins are coded for by a plasmid in Bacillus thuringiensis. Bt crystals, or insecticidal crystal proteins (ICP), are protein crystals formed during sporulation in some Bt strains (Bacillus thuringiensis ).

Bt Toxin Protein Structure
permission pending from
P. Grochulski
Homepage
Where do Bt toxins come from?
Bt toxins that are expressed in transgenic crops come from the bacteria, Bacillus thuringiensis. The various strains of Bacillus thuringiensis produce approximately two hundred different toxic crystal proteins (Bacillus thuringiensis ).
How do Bt toxins work?
Bt toxins must be eaten in order to be effective. The proteins dissolve in the highly basic insect gut (Bacillus thuringiensis ). The proteins target the intestine by binding to receptors on the intestinal cells (Bacillus thuringiensis ). The protein breaks down to release a toxin, known as delta-endotoxin. This toxin binds to the intestinal lining and creates pores resulting in ion imbalance, impaired digestion, and eventually insect death (Ed. Nott, 2003). The bacteria living in the gut exit out of the holes in the intestine and infect the rest of the body (Bacillus thuringiensis ).
GMOs and Bt
Beginning in 1996, genes for Bt crystal proteins were inserted into the genomes of plants. Consequently, these transgenic plants produce Bt crystal proteins that give the plants insecticidal properties. These plants in turn do not need insecticidal sprays applied to them. It is estimated that prices are .8¢/lb. lower from increased production due to Bt technology (Bacillus thuringiensis). See Environmental Conservation for info about less pollution.
This website was created by
Kevin Saunders, Helen Nguyen, and Chris Wrobleski
as part of an undergraduate assignment at Davidson College.
Send questions or comments to chwrobleski@davidson.edu.
© Copyright 2004 Department of Biology, Davidson College, Davidson, NC 28035.