Fall 1997 Biology 111 Exam #4 - Cancer, HIV and Transgenics
There is no time limit on this test, though I have tried to design one that you should be able to complete within 2.5 hours, except for typing. You are not allowed to use your notes, old tests, or any books, nor are you allowed to discuss the test with anyone until all exams are turned in by 5 pm on Thursday December 18. EXAMS ARE DUE BY 5 PM ON THURSDAY DECEMBER 18. Remember that I will be out of town Dec. 13-17 but will be in my office all day Dec. 18th. You may use a calculator and/or ruler. The answers to the questions must be typed on a separate sheet of paper unless the question specifically says to write the answer in the space provided. If you do not write your answers on the appropriate pages, I may not find them unless you have indicated where the answers are.
Please do not write or type your name on any page other than this cover page. Staple all your pages (INCLUDING THE TEST PAGES) together when finished with the exam.
Name (please print):
Write out the full pledge and sign:
How long did this exam take you to complete (excluding typing)?
Lab Questions:
6 pts.
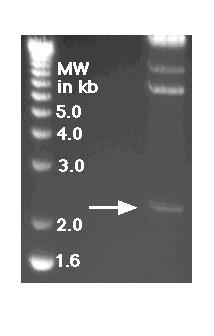
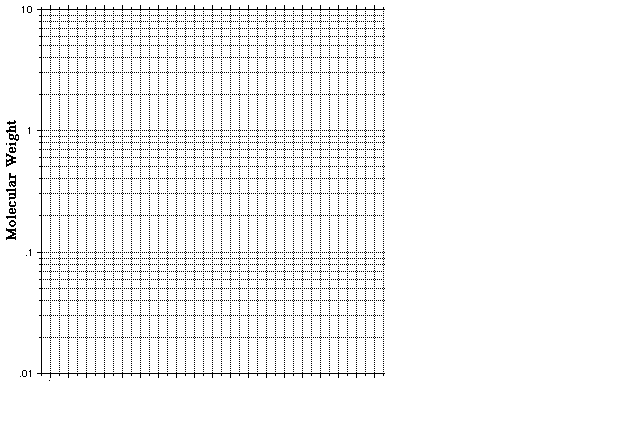
1) a. Using the graph paper provided below, calculate the molecular weight of the band indicated by the arrow.
b. This band of DNA represents a locus that contains a VNTR. If there were zero repeat units (each repeat unit is 20 base pairs long) in this target sequence, it would have been 1800 base pairs long. How many repeat units are present in this VNTR alllele?

4 pts.
2) In our lab this semester, the PCR did not work. The most likely reason is that one of the reagents was not added to the PCR mixture or had gone bad. Make a list of all the reagents used in a standard polymerase chain reaction so that we can make a check list for determining what went wrong.
Lecture Questions:
12 pts.
3) a. Describe the structure of MPF. (a picture may be useful, in addition to text)
b. Through what mechanism does the concentration of MPF rise and fall during the cell cycle?
c. What specific function(s) does MPF perform?
3 pts.
4) Give one example of a yeast cdc mutant and what phenotype the mutant cell would have if the cell lacked this gene.
4 pts.
5) Since about 85% of all cancers are not caused by viruses, why have they been so useful in understanding cancer? In other words, what did we learn about the causes of cancer by studying viruses?
4 pts.
6) How do retroviruses come to carry human genes?
8 pts.
7) Define these four terms:
a. proto-oncogene
b. oncogene
c. v-src
d. c-src
6 pts.
8) What protein does the ras proto-oncogene encode?
b. What change(s) have taken place in the function of ras when it becomes the cause of a cancer?
8 pts.
9) a. Describe the relationship between a tumor suppressor and an oncogene.
b. What is the minimum number of mutations you must have in a single cell in order to develop cancer. Explain your answer.
4 pts.
10) Which arm of the immune system is more effective against viruses and tumors? Explain your answer.
12 pts.
11) Tell me where one finds the following molecules and what the function of each molecule is:
a. reverse transcriptase
b. CD4
c. CCR5 and CXCR4 (define these two molecules together)
d. gp120 and gp41 (define these two molecules together)
6 pts.
12) What two types of drugs are used in the "triple cocktail" drug treatment for AIDS? Explain how each type of drug works.
3 pts.
13) Define the term "transgenic organism" and tell how this differs from gene therapy used to treat human diseases.
5 pts.
14) Explain the concept of a second messenger and give a specific example of one that we have studied.
5 pts.
15) What is chemiosmosis and what is produced as a result of this process?
10 pts.
16) After this semester, you might be contacted by Glaxo Welcome (an international pharmaceutical company) to design a transgenic hen that will lay eggs which contain antimicrobial proteins and thus produce Salmonella -free eggs. If it works, this would make you and the company a lot of money [and you will be hearing from the alumni office immediately]. Of course, you design a good transgene but for some reason, when the hens are fed Salmonella, the bacteria are found alive and well in the eggs and not dead in the eggs the way you had intended them to be.
Provide the company with a check list of things that could go wrong with the gene expression of this protein into the egg. In other words, list the 5 major steps of gene expression and what could go wrong with the transgene at each step.
+2 pts.
For extra credit, design an experiment that would allow you to determine if the protein is being made and is inside the egg but it is not functional for some reason.